Effect of alloying elements (Mn, Ti, and Mo) on the corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCr-based high entropy alloy in supercritical water
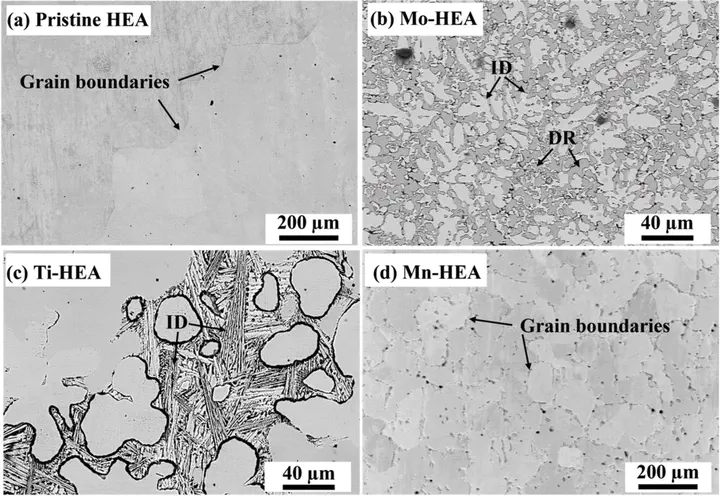 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
The effect of alloying elements, Mn, Ti, and Mo, on the corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCr-based high entropy alloy (HEA) in supercritical water was investigated. The corrosion resistance of the HEA was enhanced by adding Mo while reduced with the addition of Ti and Mn. The segregation of Ti and Mo resulted in the formation of oxide films that were both structurally and chemically heterogeneous. Grain boundaries accelerated the diffusion rate of Mn, leading to the formation of MnCr2O4 oxide scales decorated with Mn2O3 particles. In addition, the governing mechanisms of alloying elements on the corrosion behavior of HEAs were also discussed.
Type
Publication
Corrosion Science